
 Read Online or Download
Table of Contents, Index
Lecture Notes
Special Relativity Practice Problems
REVIEW
⓶ Einsteinian Relativity
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Relativity/Week2.html
Read Online or Download
Table of Contents, Index
Lecture Notes
Special Relativity Practice Problems
REVIEW
⓶ Einsteinian Relativity
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Relativity/Week2.html

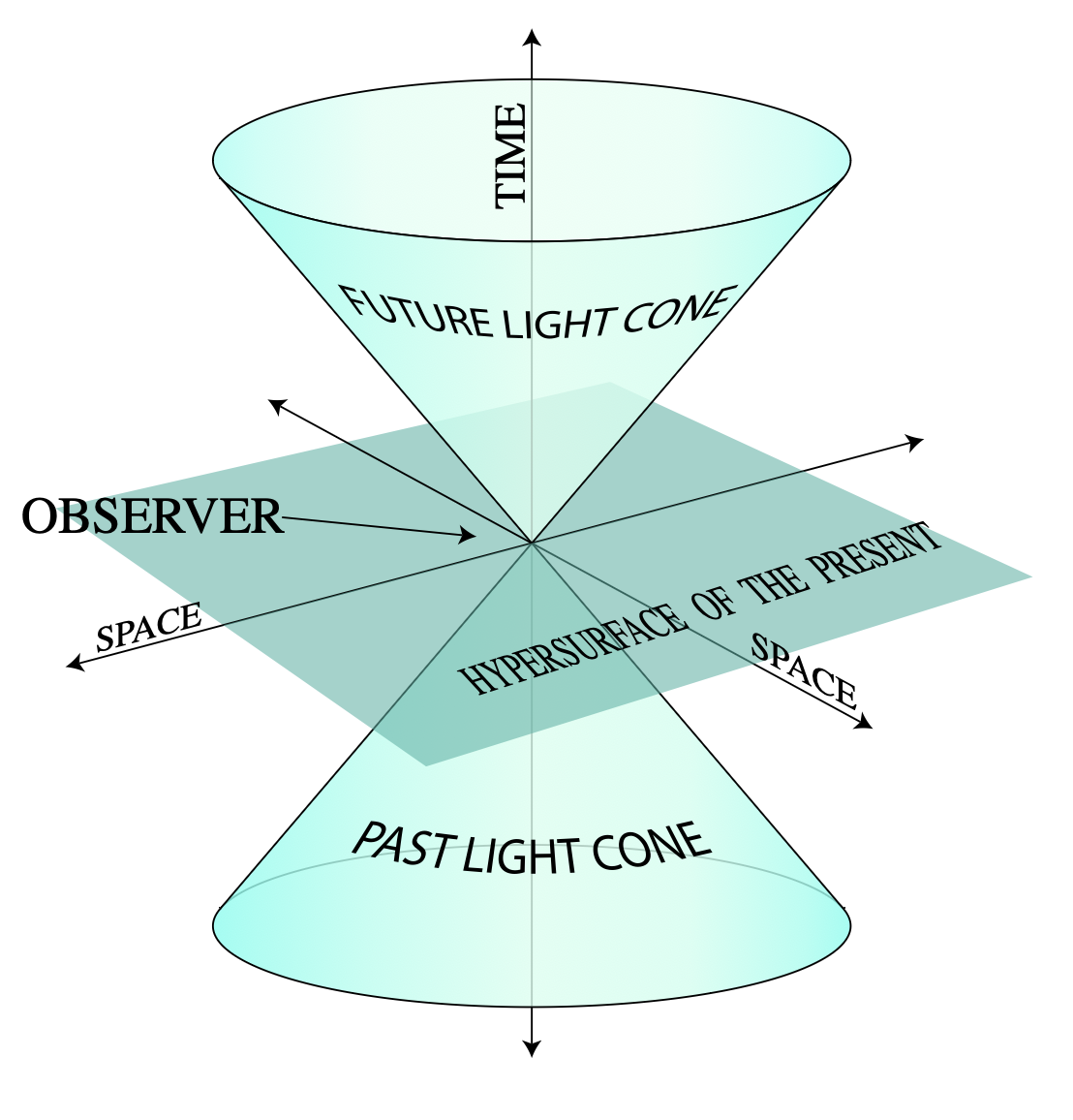 Supernovae Problem I
http://www1.phys.vt.edu/~takeuchi/relativity/practice/problem15.html
Supernovae Problem I
http://www1.phys.vt.edu/~takeuchi/relativity/practice/problem15.html
 The spacetime diagram shows five stars which go supernovae
at spacetime points A, B, C, D, and E. These supernovae are
observed by astronomers on the Earth, and also by scientists
aboard a fast moving spaceship, the trajectories of which
are also shown on the spacetime diagram.
In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in
the Earth frame of reference?
B and E simultaneously, then D, then A, then C.
In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in
the spaceship frame of reference?
E, then D, then B, then A and C simultaneously.
In which chronological order do the astronomers on Earth see
the supernovae?
B, then A, then D, then E, then C.
In which chronological order do the scientists on the
spaceship see the supernovae?
B, then D, then E, then A and C simultaneously.
Is the chronological order in which supernovae A and B occur
the same in all frames of reference? Explain.
The chronological order of A and B is the same in all frames
of reference. The spacetime points A and B can be connected
by an object or signal which travels slower than the speed
of light. (In technical terms, A is in the future light-cone
of B.) Therefore, B must happen before A in all frames.
Supernovae Problem II
http://www1.phys.vt.edu/~takeuchi/relativity/practice/problem16.html
The spacetime diagram shows five stars which go supernovae
at spacetime points A, B, C, D, and E. These supernovae are
observed by astronomers on the Earth, and also by scientists
aboard a fast moving spaceship, the trajectories of which
are also shown on the spacetime diagram.
In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in
the Earth frame of reference?
B and E simultaneously, then D, then A, then C.
In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in
the spaceship frame of reference?
E, then D, then B, then A and C simultaneously.
In which chronological order do the astronomers on Earth see
the supernovae?
B, then A, then D, then E, then C.
In which chronological order do the scientists on the
spaceship see the supernovae?
B, then D, then E, then A and C simultaneously.
Is the chronological order in which supernovae A and B occur
the same in all frames of reference? Explain.
The chronological order of A and B is the same in all frames
of reference. The spacetime points A and B can be connected
by an object or signal which travels slower than the speed
of light. (In technical terms, A is in the future light-cone
of B.) Therefore, B must happen before A in all frames.
Supernovae Problem II
http://www1.phys.vt.edu/~takeuchi/relativity/practice/problem16.html
 The spacetime diagram shows five stars which go supernovae
at spacetime points A, B, C, D, and E. These supernovae are
observed by astronomers on the Earth, and also by scientists
aboard a fast moving spaceship, the trajectories of which
are also shown on the spacetime diagram.
In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in
the Earth frame of reference?
E, then B, then A, then C and D simultaneously.
In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in
the spaceship frame of reference?
E, then B, then D, then A and C simultaneously.
In which chronological order do the astronomers on Earth see
the supernovae?
A, then B, then C and E simultaneously, then D.
In which chronological order do the scientists on the
spaceship see the supernovae?
B, then A, then C and E simultaneously, then D.
Is the chronological order in which supernovae B and D occur
the same in all frames of reference? Explain.
The chronological order of B and D is NOT the same in all
frames of reference. The spacetime points B and D cannot
be connected by an object or signal which travels slower
than the speed of light. They are outside of each others
light-cones. Therefore, their chronological order will
depend on the frame.
Supernovae Problem III
http://www1.phys.vt.edu/~takeuchi/relativity/practice/problem16.html
The spacetime diagram shows five stars which go supernovae
at spacetime points A, B, C, D, and E. These supernovae are
observed by astronomers on the Earth, and also by scientists
aboard a fast moving spaceship, the trajectories of which
are also shown on the spacetime diagram.
In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in
the Earth frame of reference?
E, then B, then A, then C and D simultaneously.
In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in
the spaceship frame of reference?
E, then B, then D, then A and C simultaneously.
In which chronological order do the astronomers on Earth see
the supernovae?
A, then B, then C and E simultaneously, then D.
In which chronological order do the scientists on the
spaceship see the supernovae?
B, then A, then C and E simultaneously, then D.
Is the chronological order in which supernovae B and D occur
the same in all frames of reference? Explain.
The chronological order of B and D is NOT the same in all
frames of reference. The spacetime points B and D cannot
be connected by an object or signal which travels slower
than the speed of light. They are outside of each others
light-cones. Therefore, their chronological order will
depend on the frame.
Supernovae Problem III
http://www1.phys.vt.edu/~takeuchi/relativity/practice/problem16.html
 The spacetime diagram shows five stars which go supernovae
at spacetime points A, B, C, D, and E. These supernovae are
observed by astronomers on the Earth, and also by scientists
aboard a fast moving spaceship, the trajectories of which
are also shown on the spacetime diagram.
In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in
the Earth frame of reference?
A and D simultaneously, then B, then C, then E.
In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in
the spaceship frame of reference?
D, then A and B simultaneously, then C and E simultaneously.
In which chronological order do the astronomers on Earth see
the supernovae?
B, then A and D simultaneously, then C, then E.
In which chronological order do the scientists on the
spaceship see the supernovae?
D, then B and C and E simultaneously, then A.
Is the chronological order in which supernovae A and E occur
the same in all frames of reference? Explain.
The chronological order of A and E is NOT the same in all
frames of reference. The spacetime points A and E cannot
be connected by an object or signal which travels slower
than the speed of light. They are outside of each others
light-cones. Therefore, their chronological order will
depend on the frame.
Interactive Minkowski Diagram
https://sciencesims.com/sims/minkowski/
Lorentz Factor Calculator 𝛾 = 1/√(1-(v^2/c^2))
https://www.azcalculator.com/calc/lorentz-factor-calculator.php
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lorentz_factor
The spacetime diagram shows five stars which go supernovae
at spacetime points A, B, C, D, and E. These supernovae are
observed by astronomers on the Earth, and also by scientists
aboard a fast moving spaceship, the trajectories of which
are also shown on the spacetime diagram.
In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in
the Earth frame of reference?
A and D simultaneously, then B, then C, then E.
In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in
the spaceship frame of reference?
D, then A and B simultaneously, then C and E simultaneously.
In which chronological order do the astronomers on Earth see
the supernovae?
B, then A and D simultaneously, then C, then E.
In which chronological order do the scientists on the
spaceship see the supernovae?
D, then B and C and E simultaneously, then A.
Is the chronological order in which supernovae A and E occur
the same in all frames of reference? Explain.
The chronological order of A and E is NOT the same in all
frames of reference. The spacetime points A and E cannot
be connected by an object or signal which travels slower
than the speed of light. They are outside of each others
light-cones. Therefore, their chronological order will
depend on the frame.
Interactive Minkowski Diagram
https://sciencesims.com/sims/minkowski/
Lorentz Factor Calculator 𝛾 = 1/√(1-(v^2/c^2))
https://www.azcalculator.com/calc/lorentz-factor-calculator.php
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lorentz_factor
 Five Papers That Shook the World
https://physicsworld.com/a/five-papers-that-shook-the-world/
ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES By A. Einstein
http://www.fourmilab.ch/etexts/einstein/specrel/specrel.pdf
Beautiful, Simple and Profound (90 min)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R_yk45m4E3M
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ASzECGtSpqQ
Spacetime: All the universe's a stage
https://www.symmetrymagazine.org/article/spacetime-all-the-universes-a-stage
Feynman Diagrams
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qe7atm1x6Mg
sam.wormley@icloud.com
Five Papers That Shook the World
https://physicsworld.com/a/five-papers-that-shook-the-world/
ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES By A. Einstein
http://www.fourmilab.ch/etexts/einstein/specrel/specrel.pdf
Beautiful, Simple and Profound (90 min)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R_yk45m4E3M
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ASzECGtSpqQ
Spacetime: All the universe's a stage
https://www.symmetrymagazine.org/article/spacetime-all-the-universes-a-stage
Feynman Diagrams
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qe7atm1x6Mg
sam.wormley@icloud.com
Read Online or Download Table of Contents, Index Lecture Notes Special Relativity Practice Problems REVIEW ⓶ Einsteinian Relativity http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Relativity/Week2.html

Supernovae Problem I http://www1.phys.vt.edu/~takeuchi/relativity/practice/problem15.html
The spacetime diagram shows five stars which go supernovae at spacetime points A, B, C, D, and E. These supernovae are observed by astronomers on the Earth, and also by scientists aboard a fast moving spaceship, the trajectories of which are also shown on the spacetime diagram. In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in the Earth frame of reference? B and E simultaneously, then D, then A, then C. In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in the spaceship frame of reference? E, then D, then B, then A and C simultaneously. In which chronological order do the astronomers on Earth see the supernovae? B, then A, then D, then E, then C. In which chronological order do the scientists on the spaceship see the supernovae? B, then D, then E, then A and C simultaneously. Is the chronological order in which supernovae A and B occur the same in all frames of reference? Explain. The chronological order of A and B is the same in all frames of reference. The spacetime points A and B can be connected by an object or signal which travels slower than the speed of light. (In technical terms, A is in the future light-cone of B.) Therefore, B must happen before A in all frames. Supernovae Problem II http://www1.phys.vt.edu/~takeuchi/relativity/practice/problem16.html
The spacetime diagram shows five stars which go supernovae at spacetime points A, B, C, D, and E. These supernovae are observed by astronomers on the Earth, and also by scientists aboard a fast moving spaceship, the trajectories of which are also shown on the spacetime diagram. In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in the Earth frame of reference? E, then B, then A, then C and D simultaneously. In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in the spaceship frame of reference? E, then B, then D, then A and C simultaneously. In which chronological order do the astronomers on Earth see the supernovae? A, then B, then C and E simultaneously, then D. In which chronological order do the scientists on the spaceship see the supernovae? B, then A, then C and E simultaneously, then D. Is the chronological order in which supernovae B and D occur the same in all frames of reference? Explain. The chronological order of B and D is NOT the same in all frames of reference. The spacetime points B and D cannot be connected by an object or signal which travels slower than the speed of light. They are outside of each others light-cones. Therefore, their chronological order will depend on the frame. Supernovae Problem III http://www1.phys.vt.edu/~takeuchi/relativity/practice/problem16.html
The spacetime diagram shows five stars which go supernovae at spacetime points A, B, C, D, and E. These supernovae are observed by astronomers on the Earth, and also by scientists aboard a fast moving spaceship, the trajectories of which are also shown on the spacetime diagram. In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in the Earth frame of reference? A and D simultaneously, then B, then C, then E. In which chronological order do the five supernovae occur in the spaceship frame of reference? D, then A and B simultaneously, then C and E simultaneously. In which chronological order do the astronomers on Earth see the supernovae? B, then A and D simultaneously, then C, then E. In which chronological order do the scientists on the spaceship see the supernovae? D, then B and C and E simultaneously, then A. Is the chronological order in which supernovae A and E occur the same in all frames of reference? Explain. The chronological order of A and E is NOT the same in all frames of reference. The spacetime points A and E cannot be connected by an object or signal which travels slower than the speed of light. They are outside of each others light-cones. Therefore, their chronological order will depend on the frame. Interactive Minkowski Diagram https://sciencesims.com/sims/minkowski/ Lorentz Factor Calculator 𝛾 = 1/√(1-(v^2/c^2)) https://www.azcalculator.com/calc/lorentz-factor-calculator.php https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lorentz_factor
Five Papers That Shook the World https://physicsworld.com/a/five-papers-that-shook-the-world/ ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES By A. Einstein http://www.fourmilab.ch/etexts/einstein/specrel/specrel.pdf Beautiful, Simple and Profound (90 min) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R_yk45m4E3M https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ASzECGtSpqQ Spacetime: All the universe's a stage https://www.symmetrymagazine.org/article/spacetime-all-the-universes-a-stage Feynman Diagrams https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qe7atm1x6Mg sam.wormley@icloud.com
