HARDWARE SECURITY
Wikipedia: Firmware
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Firmware
In computing, firmware is a specific class of computer
software that provides the low-level control for a device's
specific hardware. Typical examples of devices containing
firmware are embedded systems (running embedded software),
home and personal-use appliances, computers, and computer
peripherals.
Firmware is held in non-volatile memory devices such as ROM,
EPROM, EEPROM, and flash memory. Updating firmware requires
EPROM or flash memory to be reprogrammed through a special
procedure.

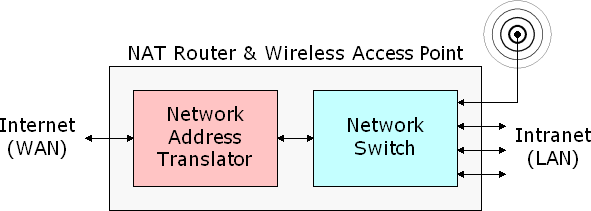 Modem Router
Modem
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Networks/Modem.html
Router
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Networks/Router.html
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Networks/Suggested_Secure_Routers.html
Modems are typically provided by Internet Service Providers
(ISPs). Some modems and routers are in the same box. When
modems and routers are separate, they are interconnected
with an ethernet cable.
Recommended settings for Wi-Fi routers and access points
https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT202068
https://www.routersecurity.org/index.php
https://www.us-cert.gov/sites/default/files/publications/HomeRouterSecurity2011.pdf
The Checklist Podcast 89: Router Rundown (22+ min)
https://www.securemac.com/checklist/checklist-89-router-rundown
Routers -- Most everybody has one at home. But most of us
don't know anything about our routers. If the router gets
hacked the bad guys can get everything!
Problems/Bugs continue to be found in hardware, operating
systems, applications software, networks, and technology.
There is an ongoing battle between the good guys finding and
fixing the problems and the bad guys1 finding and exploiting
the problems. Your role is important in this ongoing drama!
1Do bad guys include ISPs, Carriers, big tech and your own
government?
Modem Router
Modem
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Networks/Modem.html
Router
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Networks/Router.html
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Networks/Suggested_Secure_Routers.html
Modems are typically provided by Internet Service Providers
(ISPs). Some modems and routers are in the same box. When
modems and routers are separate, they are interconnected
with an ethernet cable.
Recommended settings for Wi-Fi routers and access points
https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT202068
https://www.routersecurity.org/index.php
https://www.us-cert.gov/sites/default/files/publications/HomeRouterSecurity2011.pdf
The Checklist Podcast 89: Router Rundown (22+ min)
https://www.securemac.com/checklist/checklist-89-router-rundown
Routers -- Most everybody has one at home. But most of us
don't know anything about our routers. If the router gets
hacked the bad guys can get everything!
Problems/Bugs continue to be found in hardware, operating
systems, applications software, networks, and technology.
There is an ongoing battle between the good guys finding and
fixing the problems and the bad guys1 finding and exploiting
the problems. Your role is important in this ongoing drama!
1Do bad guys include ISPs, Carriers, big tech and your own
government?
Printer Insecurity: Is it Really an Issue? Yes! (Academic)
https://www.sans.org/reading-room/whitepapers/threats/printer-insecurity-issue-1149
Seven Ways to Protect Your Printers (Practical)
https://www.pcworld.com/article/245213/7_ways_to_protect_your_business_printers.html
Invaders of the internet connected home (Academic)
https://www.sans.org/reading-room/whitepapers/internet/invaders-internet-connected-home-39855
Physical Security
http://www.us-cert.gov/sites/default/files/publications/RisksOfPortableDevices.pdf
INTERNET OF THINGS (IOT)
To ensure the security of your Internet of Things (IoT)
devices, it's crucial to follow some best practices:
1. Keep Devices and Software Updated: Regularly update your
IoT devices and software. Updates often contain security
patches that protect against new vulnerabilities.
2. Change Default Passwords: Default passwords are a common
vulnerability. Use unique, strong passwords for each device
and avoid using the same password across multiple devices.
3. Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication: Create
strong passwords and consider using a password manager.
Also, enable two-factor authentication whenever possible to
add an extra layer of security.
4. Wi-Fi Network Security: Change your router's default name
and use a strong encryption method like WPA2 or later for
your Wi-Fi network. Additionally, consider setting up a
separate guest network for your IoT devices.
5. Device Management and Monitoring: Keep track of all IoT
devices in your network and monitor them for suspicious
activities. Implement continuous monitoring software to
manage and secure these devices effectively.
6. Cryptography and Segmentation: Use suitable cryptography
methods for data protection and consider segmenting your
network to isolate IoT devices, which helps in containing
breaches and reducing network congestion.
7. Privacy Settings and Feature Management: Review and
adjust the privacy settings of your IoT devices. Disable any
unnecessary features to reduce potential attack vectors.
8. Data Encryption and Identity Management: Encrypt
sensitive data and use identity management solutions to
ensure only authorized devices have access to critical data.
9. Regular Firmware Updates: Ensure that your devices are
regularly updated with the latest firmware to protect
against security threats.
10. Secure Network Configuration: Secure your network by
changing default passwords, using strong encryption,
updating router firmware, enabling firewalls, and monitoring
for unusual activity.
11. Disable Remote Management Features: Turning off
unnecessary remote management features can prevent
unauthorized access to your router and network.
These practices will help in minimizing the risks associated
with IoT devices and ensure their secure use. Remember, IoT
security is an ongoing process and requires regular
attention and updates to stay effective.
WHAT HARDWARE CAN SPY ON YOU?
http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Privacy/index.html#SPY
NSA: BEST PRACTICES FOR SECURING YOUR HOME NETWORK
https://media.defense.gov/2023/Feb/22/2003165170/-1/-1/1/CSI_BEST_PRACTICES_FOR_SECURING_YOUR_HOME_NETWORK.PDF
sam.wormley@icloud.com

Modem Router Modem http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Networks/Modem.html Router http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Networks/Router.html http://edu-observatory.org/olli/Networks/Suggested_Secure_Routers.html Modems are typically provided by Internet Service Providers (ISPs). Some modems and routers are in the same box. When modems and routers are separate, they are interconnected with an ethernet cable. Recommended settings for Wi-Fi routers and access points https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT202068 https://www.routersecurity.org/index.php https://www.us-cert.gov/sites/default/files/publications/HomeRouterSecurity2011.pdf The Checklist Podcast 89: Router Rundown (22+ min) https://www.securemac.com/checklist/checklist-89-router-rundown Routers -- Most everybody has one at home. But most of us don't know anything about our routers. If the router gets hacked the bad guys can get everything! Problems/Bugs continue to be found in hardware, operating systems, applications software, networks, and technology. There is an ongoing battle between the good guys finding and fixing the problems and the bad guys1 finding and exploiting the problems. Your role is important in this ongoing drama! 1Do bad guys include ISPs, Carriers, big tech and your own government?